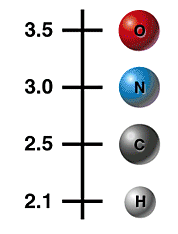
Electronegativity Scale
Polar Covalent Bond
An atom's tendency to attract electrons is called electronegativity. Atoms near the top of the scale attract electrons more strongly than atoms near the bottom. For instance, when O and H form a bond, O pulls electrons towards itself, creating a partial negative charge. This leaves the H with a partial positive charge. The result is a polar covalent bond.